Describe the Role of Platelets in Hemostasis and Blood Clotting
A fibrin b fibrinogen c thrombin d prothrombin e plasmin. The process of blood clotting and then the subsequent dissolution of the clot following repair of the injured tissue is termed hemostasis.
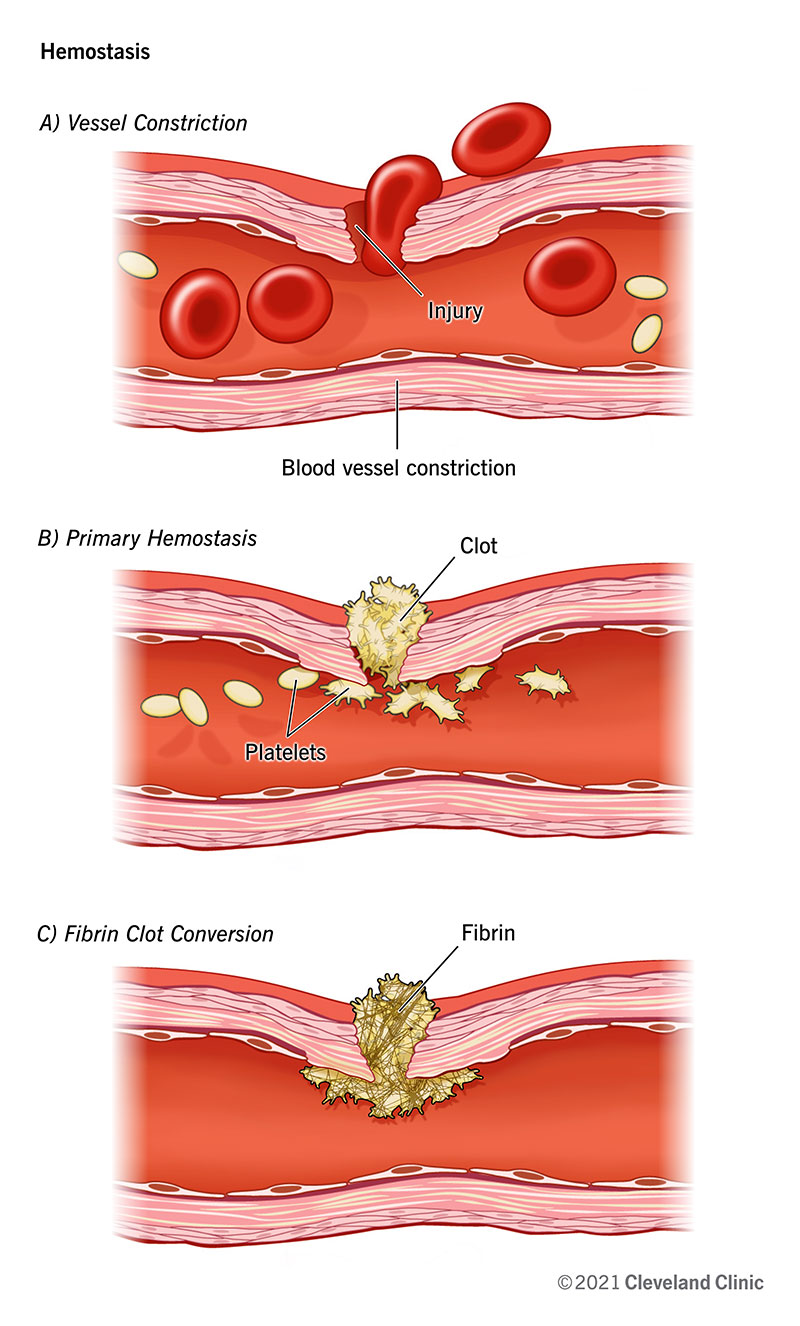
Hemostasis Stages And How The Process Stops Blood Flow
Describe role of platelets in haemostasis Outline the mechanism of platelet plug formation.
. Vasoconstriction is a reflex in which blood vessels narrow to increase blood pressure. Describe what occurs in each of the steps below beginning with injury and ending with blood clot formation. Although rupture of larger vessels usually requires medical intervention hemostasis is quite effective in dealing with small simple wounds.
1 vascular spasm vasoconstriction. Coagulation on PL surface. As a part of normal activities small blood vessels often break and a platelet plug is usually sufficient to stop the bleeding.
Describe the main mechanisms that prevent blood loss after an injury. Platelets are central to both normal hemostasis and abnormal thrombotic states along with the vessel wall coagulation elements and blood flow. Clot FormationReinforces platelet plug and converts blood in the vicinity of vessel injury into a non flowing gelClotting factors are always present in blood plasma in inactive precursor formVessel damage that exposes collagen initiates cascade of reactions that involve successive activation of clotting factors finallyConvert fibrinogen fibrin by means of the.
Hemostasis comprises four major events that occur in a set order following the loss of vascular integrity. View the full answer. Clot FormationReinforces platelet plug and converts blood in the vicinity of vessel injury into a non flowing gelClotting factors are always present in blood plasma in inactive precursor formVessel damage that exposes collagen initiates cascade of reactions that involve successive activation of clotting factors finallyConvert fibrinogen fibrin by means of the.
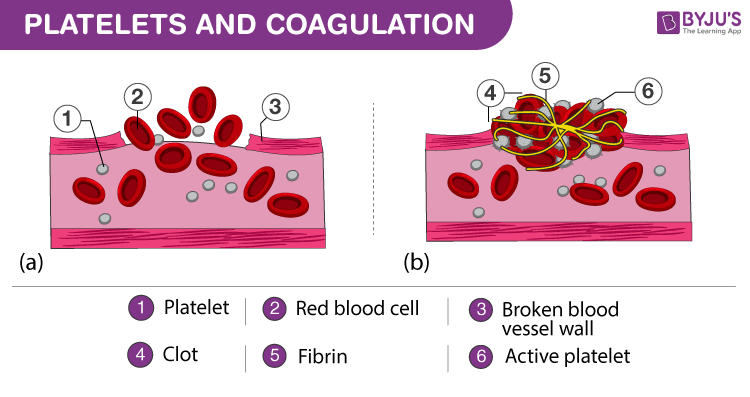
In the clotting process _____ forms a mesh that traps blood cells and platelets. A coat of glycoprotein receptors that cause adherence to injured endothelial cells and exposed collagen. Phospholipids that play an important role in blood clotting.
2nd Year Physiotherapy- November 2008 9 Functional characteristics of platelets The cell membrane of platelets contains. Hemostasis facilitates a series of enzymatic activations that lead to the formation of a clot with platelets and fibrin polymer. Platelets participate in maintaining normal hemostasis of keeping the blood in fluid state but mainly known for the constriction and repair of damaged blood vessels to prevent the loss of blood.
The main function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis. Platelets contribute their hemostatic capacity through adhesion activation and aggregation all of which are initiated by tissue injury and stimulate the coagulation factors and other mediators needed to achieve hemostasis. 2 platelet plug formation.
Hemostasis Hemostasis is a physiological defensive reaction to an injury or a cut that seals the blood vessels and thus helps in healing Mainly platelets endothelial cells of blood vessels and blood proteins are responsible for hemostasis. It is necessary for maintaining the bodys overall function. Shape change to pseudopod.
Platelet Plug Formation 4. Release or secretion of dense bodiesalpha granules. The number of platelets in the blood varies between 150-350 x10 9 L.
Thus the platelets help in blood coagulation. Although rupture of larger vessels usually requires medical intervention hemostasis is quite effective in dealing with small simple wounds. Swell Form pseudopods Become contractile and.
The initial phase of the process is. Secondary hemostasis stabilization of platelets plug by fibrin fibrin formation by coagulation factors within several min. Platelets also participate in pathological processes and associated with thrombosis bleeding growth of.
The classic description of coagulation involved a cascade model consisting of two distinct pathways. What initiates platelet aggregation and activates receptors exposed in damaged endothelium by the binding of platelets to the activated receptor inducing physical changes thrombin activates thrombin receptors exposed in damaged endothelium and these thrombin activated receptors bind platelets which release factors like von Willebrandfactor linking exposed thrombin. Lets look at.
Primary hemostasis platelet reactions and primary hemostasis plug formation unstable plug within few first minute temporal control. What role does serotonin play in hemostasis. This clot seals the injured area controls and prevents further bleeding while the tissue regeneration process takes place.
Describe the three major steps involved in. Platelet comes in contact with collagen fibers in the damaged vessel and is activated to. The extrinsic or tissue factor pathway and the intrinsic.
Describe the mechanisms of blood coagulation 2nd Year Physiotherapy-November 2008 2. The platelets play a pivotal role in the reaction that occurs after vessel injury during which platelets first adhere to the vessel wall undergo a release reaction and then aggregate probably as a result of the materials released from platelets. Role of platelets in hemostasis.
Hemostatic mechanism proceeds in the following series of steps. They gather at the site and unless the interruption is physically too large they plug the hole. Blood clotting is aided by platelets stopping bleeding.
In addition to their role in primary hemostasis activated platelets provide an efficient catalytic surface for the assembly of the enzyme complexes of the blood coagulation system also known as secondary hemostasis. Platelets are key players in hemostasis the process by which the body seals a ruptured blood vessel and prevents further loss of blood. Platelets are key players in hemostasis the process by which the body seals a ruptured blood vessel and prevents further loss of blood.
The entire process is referred to as hemostasis which translates into blood halting. Be sure to mention 1. Become sticky attracting more and more platelets.
The process of stopping bleeding at the site of interruptedendothelium. Platelet counts are low in people with thrombocytopenia. Binding to damaged endothelium.
Next platelet plug formation involves the activation aggregation and adherence of platelets into a. First platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium. 5 Homeostasis in the body means maintaining the correct temperature balance of ions in the blood a steady blood pH correct level of blood glucose the right blood pressure etc.
Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occursIt involves three steps. The process involves platelets or cells that clump together to help stop bleeding.

Platelets Coagulation And Hemostasis An Overview

Hemostasis Anatomy And Physiology Ii
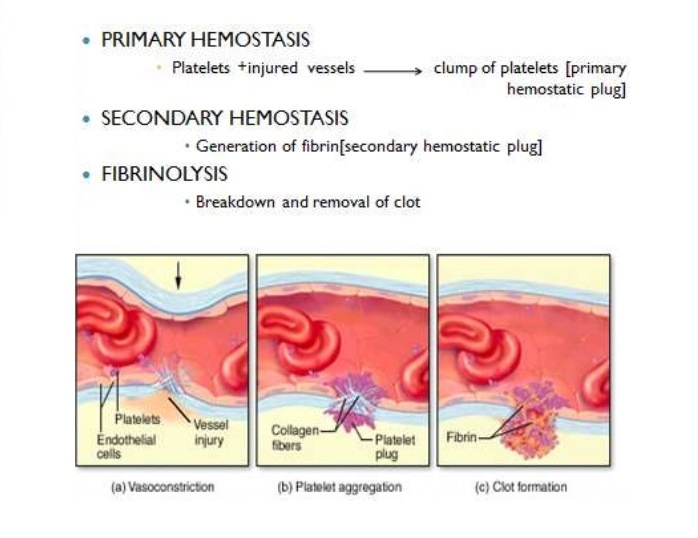
Hemostasis Vascular Spasm Clot Retardation Formation Of Platelet Plug Blood Clot Science Online
Comments
Post a Comment